5 Potent Diseases of Poultry Birds and How to Overcome Themt
Some diseases affect poultry birds and can sometimes be severe and life-threatening. These diseases affect the overall well-being of your birds: the growth rate, egg and meat production, and physical appearance. We understand how important producing quality birds is to poultry farmers, hence the guide to help poultry farmers identify the different types of poultry diseases in poultry farming.

Bacteria-causing diseases
Bacterial diseases in poultry farms are contracted by physical contact with infected birds and disease hosts like pigs and rodents. These diseases are also transmitted by contaminated poultry equipment and from hen to chick during breeding or hatching.
Bacterial diseases can be curbed when you identify the symptoms on time, and separate the affected birds for treatment, or, better still, contact a vet doctor.
Some of the more popular bacterial-causing diseases are fowl cholera, caused by Pasteurella multocida, fowl typhoid, caused by Salmonella gallinarum, pullorum disease, caused by Salmonella pullorum, and mycoplasmosis.

Viral-causing diseases
Viral diseases in poultry farms include fowl pox, chicken infectious anemia, avian encephalomyelitis, Marek disease, and egg drop disease.
Avian influenza, Newcastle disease, and infectious bronchitis affect the respiratory tracts of poultry birds.
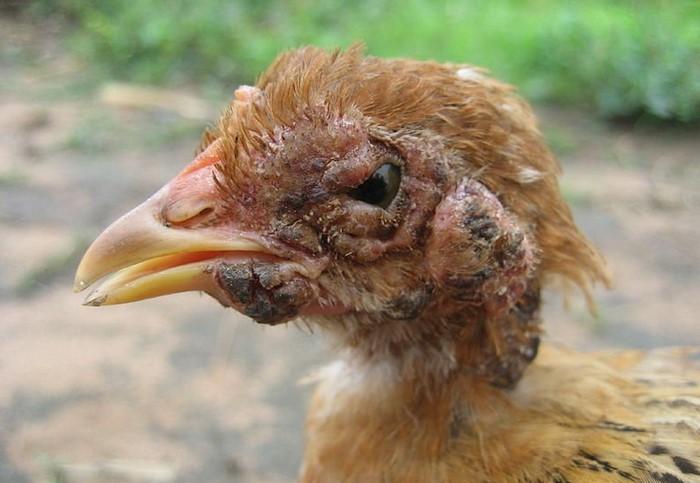
Fungal-causing diseases
Fungi grow on soil surfaces, rotten feed, and air. Then, they multiply and develop all over the surroundings of the farm. When poultry birds contact surfaces where these fungi are bred or breathe in the contaminated air, they become affected.
Fungal diseases are also said to grow primarily in the lungs or skin of poultry birds. Popular fungal diseases that affect poultry are Aspergillus fumigatus, candidiasis, and zygomycosis.

Parasite-causing bacteria
Parasites are organisms that live and feed on other organisms. Some parasites live in the internal bodies of animals, and they are known as “internal parasites,” while parasites that live outside the bodies of other animals are known as “external parasites.” Protozoa parasites like Coccidia live in the digestive tracts of poultry birds.
Internal parasites that affect poultry birds are worms and protozoa. Roundworms, cecal worms, gapeworms, and tapeworms also affect poultry birds. The external parasites in poultry birds are lice and mites.

Deficiency-causing diseases
Vitamins, proteins, and minerals are essential for normal growth in poultry. When these vitamins and minerals are absent, poultry birds suffer malnutrition.
Vitamins are important for general well-being, strong bones, beak formation, and blood production. They also serve as antioxidants. So, you can be sure to expect some ailments when they are absent.
The deficiency of these vitamins and minerals in poultry feed can result in decreased egg production, loss of weight, increased embryonic mortality, and growth. Crazy chicken disease is a commonly known deficiency disease caused by the deficiency of Vitamin E in poultry feed.
In all, good feed that contains all the required nutrients is highly recommended to prevent diseases caused by a deficiency of nutrients.
Bacteria-causing diseases
Depending on the stage and severity of the disease, symptoms can differ. Below are some of the more noticeable symptoms of diseases in poultry birds:
● Coughing, sneezing, and eye and nose discharge
● Lack of appetite and a notable weight loss
● Irregular growth
● Face and joint swelling
● Body fever
● Reduction in egg production.
● Difficulty in respiratory operations or breathing
● Inactivity affects birds.
● feather, tail, and wing loss
● Dehydration
● Anemia
● Death
Preventive measures against diseases in poultry farming
The good news is that poultry farmers can guard against the different diseases mentioned above. Check out some of the ways to prevent these diseases.
Good living conditions:Farmers should ensure that poultry birds have enough space in the poultry house. This is because proper spacing prevents overcrowding and reduces disease transmission. Also, soft bedding and enough light should be provided for the birds.
Feed and water: Provide a clean water system and quality feed that meets the birds’ nutritional needs. Antifungal medications should be administered to treat fungal diseases.
Vaccination:The administration of vaccines helps to prevent the sporadic spread of diseases on poultry farms. Some of these vaccines effectively guard against avian encephalomyelitis, chicken anemia, fowl pox, and infectious coryza. Also, make sure to buy only appropriately vaccinated poultry birds when starting your poultry farm.
DeWorming: As a preventive measure, poultry farmers are advised to deworm their birds at least once a year to prevent diseases caused by internal parasites.
Use of pesticides/insecticides: Pesticides or insecticides are chemicals used to control external parasites around the farm’s surroundings. Use disinfectant when poultry birds are far away from the farm surroundings to avoid close contact with the chemicals.
Segregating sick birds: Separate sick or infected birds to prevent the spread of diseases. You can use the symptoms mentioned above to easily identify sick birds.
Proper observation: You can avoid the spread of diseases in your poultry farm. For instance, worms are easy to detect in bird droppings.
In Summary
Only healthy poultry birds bring good income. Therefore, poultry birds’ health should be prioritized in a poultry farm business. As earlier mentioned, there are different kinds of poultry diseases, and they are grouped according to the causative agents. The symptoms, treatment, and preventive measures have been discussed in this resource. So, ensure that you maintain good hygiene and sell only the best poultry products to consumers.